Many people face a diagnosis of osteochondrosis in the lower back.Symptoms of this disease: constant pain in the lower back, as well as limited movements, loss of sensitivity and so on.Anyway, it should be understood that this disease in the absence of treatment can lead to a mass of neurological complications.So what is the disease?What are your first signs?What treatment methods does modern medicine offer?This information will be useful for each reader.
What is osteochondrosis?
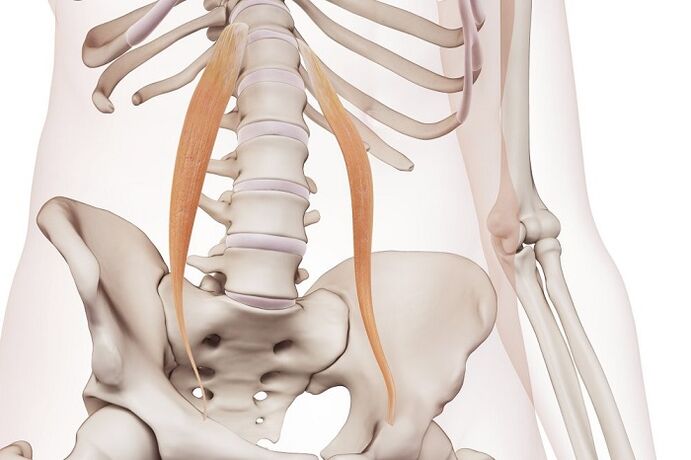
Osteochondrosis is a chronically progressive disease that is accompanied by the degeneration of connective and bone tissues of the spine.The process of pathological changes in tissues begins on the intervertebral disc.This structure consists of a fibrous ring, within which there is a Pulpic nucleus of the gel type.
As a result of a violation of normal metabolism, there is a gradual drying of the nucleus.Along with this, the changes are also observed in the fibrous ring: tears and cracks are formed in tissues as a result of which the core can go beyond.A similar process affects the state of vertebrates because vertebrae need to withstand heavy loads.Thus, not only intervertebral discs, but also vertebrae, ligaments and intervertebral joints are involved in the process.
As a rule, the disease begins in adulthood or old age, although there are cases where the disease has been diagnosed in adolescents.By the way, lumbar osteochondrosis is the most common form of this disease.
The causes of disease development
This pathology develops with a violation of normal metabolism and the presence of increased physical effort.It is worth noting that the degenerative process, as a rule, is launched under the influence of several factors at the same time.So far, lumbar osteochondrosis is considered a multifactorial disease.Here are only the most common causes of degeneration.
- First of all, one should notice a hereditary predisposition.The cause may be some of the congenital anatomical characteristics of the skeleton and metabolic disorders, such as the wrong metabolism of glycoproteins.
- Risk factors include flat feet, because with this pathology there is a redistribution of the normal load in the spine.
- In some cases, osteochondrosis develops at the bottom of spinal lesions.
- Static loads can also be attributed to risk factors.For example, longtime or remaining in an uncomfortable position.
- Physical tension can also initiate a degenerative process, especially when it comes to professional athletes.
- Often the process develops in obese people, since the spine, as well as the whole skeleton, lends itself to increasing loads.
Severity of osteochondrosis lumbar
This disease develops gradually.To date, it is usual to distinguish four major degrees of lumbar osteochondrosis (some doctors emit three).
- In the first stage, there is a gradual change and movement of the jacket core within the intervertebral disc.
- Lumbar osteochondrosis of the 2nd degree is characterized by the destruction of the fibrous ring.
- In the third stage, as a rule, there is a break from the fibrous ring, as a result of which the gelatinous core moves beyond its limits, so that the intervertebral hernia is formed.
- The fourth stage of the disease is accompanied by degeneration of vertebrae, ligaments and joints, as a result of which spondylartrosis develops.
Lumbar osteochondrosis: symptoms and description of the first stage of the disease
This stage of the disease is accompanied by irritation of nerve fibers, which are in interdustrian ligaments and in a fibrous ring.Therefore, the first sign of this disease is discomfort, stiffness and pain in the lower back.It is worth noting that the pain can be hard and shoot (in medicine, this symptom is called "lumbago") or, on the contrary, stupid but constant (lumbalgia).
It is worth noting that due to the irritation of nerve endings, pain can also be extended to other tissues, organs or even organ systems.For example, in case of violation of normal tropism and blood circulation in ligaments and tendons, the appearance of enteropathies called SO may occur in which connective tissues change and compress in bone fixation sites.
As often in patients, lumbosacral osteochondrosis is diagnosed, pain can apply to the lower spine and even give to the lower limb.Compression of nerve endings and small vessels leads to the development of violations in the tissues of the lower extremities.
The second degree of osteochondrosis and its signs
At this stage, some other signs of lumbar region osteochondrosis appear.The appearance of a certain instability between the vertebrates is observed, as a result of which the mobility of the vertebrae increases.
In turn, this change leads to the occurrence of persistent and almost constant tension of the lumbar muscles.Patients complain not only about pain and discomfort, but also for constant muscle fatigue.
Clinical image with the third degree of disease

What signs in this case are accompanied by lumbar osteochondrosis?Symptoms during this period may be different.The fact is that damaged intervertebral discs begin to squeeze the nerve roots, which are accompanied by the "root syndromes."
At the same time, patients interrupt the sensitivity of the zones that are innervated by a compressed nerve.As a rule, slight numbness and tingling occur at first, but in the absence of treatment, complete loss of sensitivity may occur.This is usually accompanied by a deterioration of motor activity, the gradual atrophy of the muscles and sometimes complete paralysis.
By the way, based on the location of such changes, we can assume which vertebrae are affected by the disease.For example, if change or loss of sensitivity is observed in the heel and the pain gives the calf muscle, the patient is likely to have lumbosacro osteochondrosis.
In some patients, the "horse tail syndrome" is observed, which is associated with root beam compaction, which occurs in the lumbar and sacral section of the spine.This condition is characterized by a violation of the motor function of the legs as well as various disorders of the pelvic organs.
Lumbar osteochondrosis: Symptoms of the fourth step
At this stage, all intervertebral joints and ligaments are already involved in the process.In addition, there is a fibrosis of the intervertebral disc, in which all its elements are replaced by a dense scar tissue.
By the way, at this time, patients from patients can improve.But the mobility of the spine, the lower back and the legs is very limited.
Modern diagnostic methods
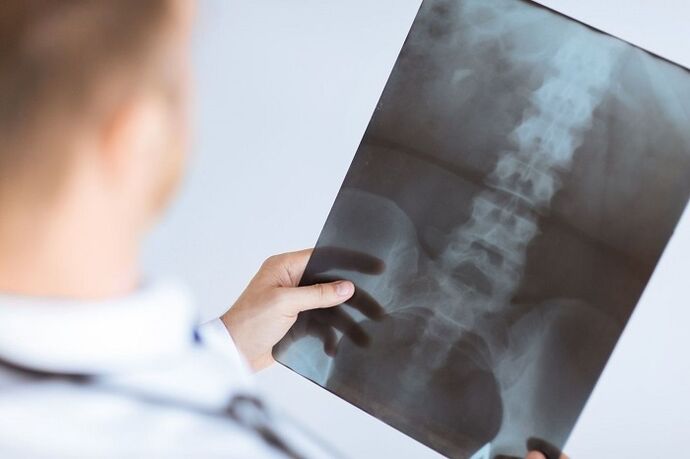
In the presence of constant pain and discomfort in the lower back, you should consult a doctor.Only one expert can determine the back of the spine.The diagnosis in this case includes various stages.
To begin with, the doctor will conduct a general examination, check the reflexes, the presence of root syndromes, as well as the degree of mobility and so on.It is necessary to collect a complete history, because in this case it is important not only to make a diagnosis, but also to determine the cause of the development of a degenerative process.
Diagnostic laboratory methods in this case are not very important.Therefore, the patient is mainly directed to the radiograph of the spine.X -ray images allow you to see the narrowing of the intervertebral slit as well as determine the presence of bone growths and seals on the surface of the vertebra.
For a more accurate assessment of the patient's condition, magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are also performed, these studies provide a clearer image of degenerative changes in the spine.
What complications is the disease associated?
In no case, should this disease perceive this frivolous disease.In the absence of timely therapy, the patient will have to face not only pain and limitation of mobility, but also with more serious consequences.
In particular, the degeneration of intervertebral discs leads to the formation of a hernia.In addition, compression of nerve roots affects the work of many organs, including urinary, sexual and sometimes digestive systems.In some cases, the disease leads to complete paralysis of the lower ends and muscle atrophy.Changes in osteochondrosis are practically irreversible, so it is extremely important to start therapy over time.
Drug treatment of osteochondrosis

Only the doctor knows how to treat lumbar osteochondrosis.With this disease, therapy is selected individually, as it depends on many factors, including the individual characteristics of the patient's body.Anyway, it should be understood that the treatment of osteochondrosis is a long and complex process.
Obviously, patients are prescribed for some medications.Most of the time, this disease is used below.
- In the early stages of treatment, condrotectors - medicines that inhibit the process of degeneration of the cartridge tissue are used.
- In the second stage, the treatment of lumbosacral osteochondrosis may include the use of anti-inflammatory drugs that eliminate pain and the inflammatory process.
- Muscle spasm is eliminated with muscle relaxants.
- Local anesthetics are used for intense pain.For example, pain is blocked with painkillers injections.
- Older patients are recommended to take multivitamin complexes.
- Therapy also includes vasodilators that improve blood circulation and trophic tissue.
Other conservative treatment methods

Obviously, it is impossible to get rid of the disease only with drug help.The treatment of osteochondrosis lumboscro includes other measures.In particular, a therapeutic massage gives a positive effect.Regular sessions help eliminate muscle spasm and improve blood circulation in tissues.
Gymnastics with lumbar osteochondrosis is extremely important.The set of exercises is selected by the doctor or participating physiotherapist.Physical education helps to return mobility, improve blood circulation, eliminate pain.Of course, classes must be regular.On the other hand, in the presence of acute pain, physical activity is against -during this period the patient needs harsh rest and use a special score, which relieves the load of the spine.
In addition, some physiotherapy methods are also used.In particular, ultraviolet radiation is considered quite effective (eliminates spasm and pain), magnetotherapy, laser therapy, electrophoresis (help alleviate inflammation and pain) as well as ball treatment.
When is surgical intervention necessary?

Unfortunately, not in all cases, conservative treatment is possible, especially if the patient has a diagnosis of intervertebral hernia.Indications for surgical intervention are also "bone tail" syndrome as well as severe compression of nerve roots.
So far, there are many techniques for these operations.Most of the time, called microcurgical, as well as endoscopic procedures, are also performed to eliminate pressure in blood vessels and nerves.


















